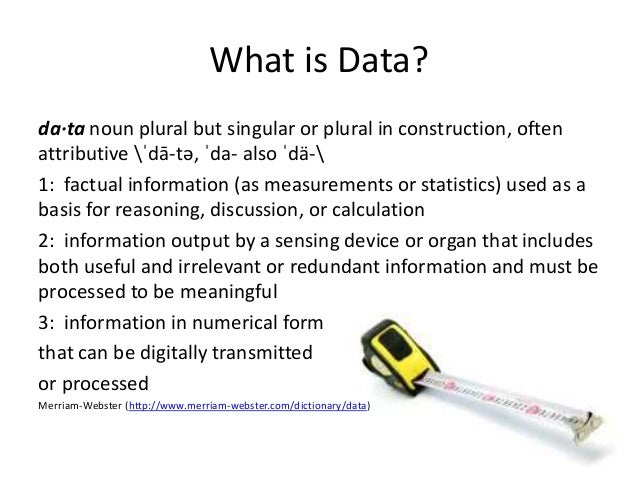
What is Data?
Types of Data
What are Statistics?
Statistics are created from numerical data that has been analyzed in some way. They are the results of data analysis. They answer questions such as "how much" or "how many. They come in:
-
tables, charts, graphs
-
within texts of a book or article

Source: Finding Datasets and Statistics
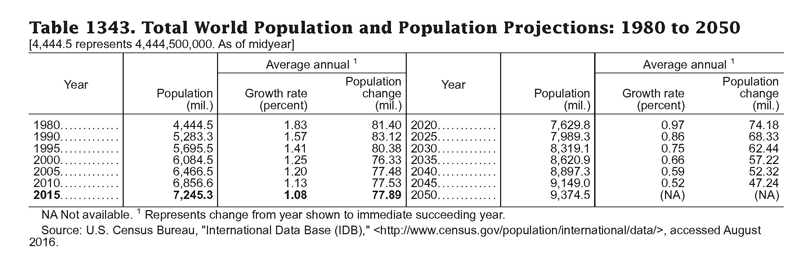
Statistics - Examples

More Definitions
Aggregate data (summary- level data): statistical summaries of data. It has been analyzed in some way. Examples: inflation rate, consumer price index
Raw data (micro-level data): individual response data collected directly from surveys or questionnaires. It has not been analyzed. Examples: census, poll and survey
Time series data: collected over time and arranged in chronological order. Example: unemployment rate over the past 30 years
Cross-sectional data: collected by observing many subjects (city, state, country) at the same point of time. Example: unemployment rate by state
Dataset: any raw data file and any related files that require statistical analysis by special software such as Excel or SPSS.


 Click to chat online now
Click to chat online now Chat is offline
Chat is offline

